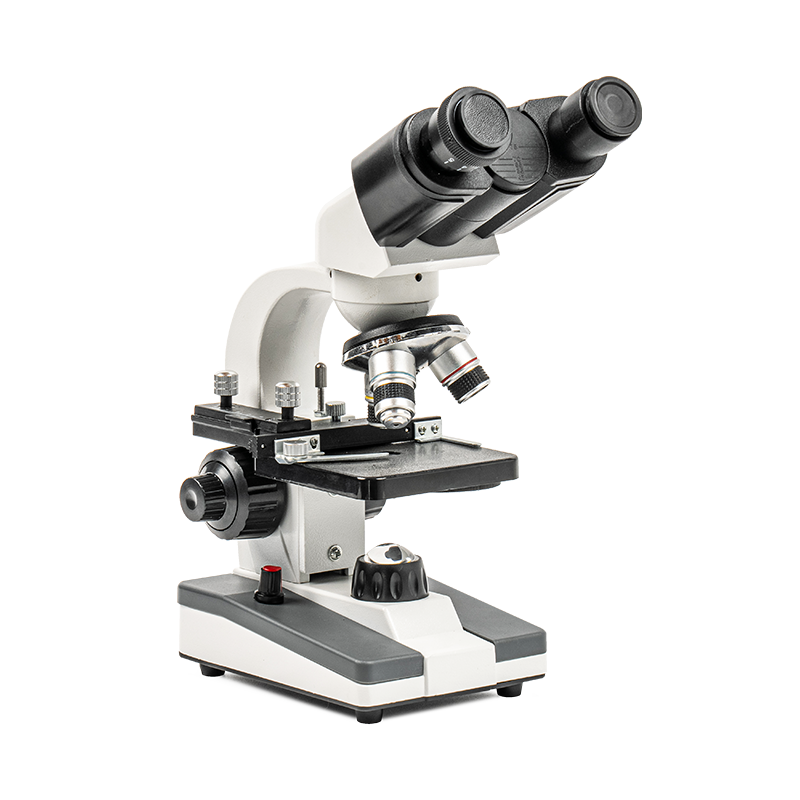
In scientific research, precision is paramount. Whether you're studying cellular structures, conducting material analysis, or investigating biological processes, accuracy in your observations is crucial. The microscope is one of the most fundamental tools in a laboratory, and selecting the right one can significantly impact the accuracy and quality of your research. The microscope for lab work you choose determines the level of detail you can observe, the clarity of your images, and ultimately the reliability of your findings.
Content
- 1 The Importance of Clarity and Resolution in Lab Research
- 2 Different Types of Microscopes for Different Research Needs
- 3 Magnification and Depth of Field: Balancing Detail with Focus
- 4 Lighting and Contrast: Key to Clear, Accurate Observations
- 5 The Role of Digital Imaging in Enhancing Research Accuracy
- 6 Stability and Durability: Ensuring Consistency Across Experiments
The Importance of Clarity and Resolution in Lab Research
The primary function of a microscope is to reveal fine details that are not visible to the naked eye. Whether you're examining cells, microorganisms, or the internal structure of materials, a microscope allows you to see and measure these components at magnifications ranging from 10x to over 1000x or more. However, the level of magnification is only one part of the equation; resolution is equally important.
Resolution refers to the ability of a microscope to distinguish between two points that are close together. A microscope with poor resolution may blur details, making it impossible to accurately interpret observations. High-quality microscopes with superior optics, like plan achromatic lenses or apochromatic objectives, can provide clearer, sharper images, ensuring that your research is based on precise and accurate observations.
A microscope with excellent resolution can reveal fine details such as cell boundaries, tiny organisms, or minute structural variations in materials, leading to more accurate conclusions and less risk of error in your research.
Different Types of Microscopes for Different Research Needs
Not all microscopes are created equal, and choosing the right type for your specific research needs is essential for achieving high-accuracy results. Different types of microscopes offer varying features and capabilities suited for different scientific disciplines:
- Light Microscopes: These are the most common type of microscope used in many laboratories. They are ideal for examining live cells, tissues, and other transparent biological samples. The quality of the lenses, as well as the light source used, can significantly affect the clarity and accuracy of your images.
- Fluorescence Microscopes: Used in biological research, fluorescence microscopes use special lighting to excite fluorescent dyes in samples. This is especially useful for studying specific cellular components or proteins. The ability to accurately distinguish fluorescence signals in different parts of the sample improves the accuracy of experiments that depend on precise molecular identification.
- Electron Microscopes (SEM/TEM): For extremely high magnifications and detailed imaging at the nanoscale, b and transmission electron microscopes (TEM) are used. These microscopes provide unrivaled resolution and are essential for applications such as materials science, nanotechnology, and cellular ultrastructure research.
- Confocal Microscopes: Confocal microscopy uses lasers to scan specimens in a focused beam of light, capturing high-resolution 3D images. This type of microscope allows researchers to observe thick samples with better optical sectioning and fewer blurs, ensuring more accurate analysis of biological tissues or complex materials.
By selecting the right type of microscope for your research needs, you can improve the precision and quality of your findings, ensuring that your conclusions are based on accurate data.
Magnification and Depth of Field: Balancing Detail with Focus
While magnification is an important factor in determining how much detail you can observe, it can also have limitations. As you increase magnification, the depth of field decreases, which can make it more challenging to maintain focus across the entire sample. This can lead to blurry or incomplete data.
For instance, when examining cell layers or complex biological specimens, having a good depth of field ensures that you can focus on the full structure of the sample at once, without needing to adjust the focus constantly. In such cases, microscopes with adjustable numerical aperture (NA) and good optical coherence offer the best balance of magnification and depth of field, improving research accuracy by allowing you to see fine details clearly without losing focus on other parts of the sample.
Some advanced microscopes, like stereo microscopes, are designed to maintain a larger depth of field at lower magnifications, making them ideal for examining three-dimensional objects or conducting dissection and other types of analysis where full focus across multiple levels of the sample is important.
Lighting and Contrast: Key to Clear, Accurate Observations
Effective lighting is essential for high-quality imaging and accurate research. Proper illumination can enhance the contrast in your sample, allowing fine details to stand out more clearly. In biological and materials science research, the clarity of these features directly influences the accuracy of the results.
In light microscopes, the light source and condenser system are critical in providing consistent, even lighting. Researchers need to ensure that the lighting is bright enough to illuminate the specimen without overexposing it or causing distortion in the image. LED lighting systems are now commonly used in many modern microscopes, offering better consistency and color accuracy compared to older incandescent light sources.
In addition to general lighting, the use of specialized techniques such as differential interference contrast (DIC) or phase contrast microscopy can enhance the visibility of transparent or colorless samples. These contrast-enhancing methods allow researchers to observe specimens like living cells in their natural state without the need for staining, which could potentially alter or damage the sample. These techniques help produce high-contrast, sharp images that are critical for accurate analysis.
The Role of Digital Imaging in Enhancing Research Accuracy
In modern research labs, the integration of digital imaging systems with microscopes is becoming increasingly popular. Digital microscopes or those equipped with cameras allow researchers to capture high-quality images and videos, which can then be analyzed and measured for precise data collection.
Digital imaging offers several advantages for research accuracy:
- Improved Documentation: With digital images, researchers can easily store, organize, and compare data over time. Images can be annotated, marked, and shared with collaborators for further analysis, ensuring that no important details are overlooked.
- Enhanced Image Processing: Digital microscopes often come with software that allows users to adjust contrast, brightness, and resolution after capturing an image, which can reveal additional details and improve accuracy. Image-processing tools like image stitching, 3D reconstruction, and quantitative measurements enable precise analysis, leading to better research outcomes.
- Real-Time Feedback: Digital microscopes allow researchers to view the specimen in real-time, making it easier to adjust focus, lighting, and magnification settings on the fly. This live feedback ensures that researchers can make on-the-spot decisions to improve image quality and accuracy.
Stability and Durability: Ensuring Consistency Across Experiments
Consistency is critical in scientific research. The right microscope should not only offer excellent optical performance but also be durable and stable enough to withstand long hours of use in the lab. A stable microscope with a strong, vibration-free stand and a reliable focusing mechanism ensures that measurements are consistent and accurate across multiple experiments.
High-quality microscopes are designed to maintain precision and offer stable mechanical performance over time. Whether you are conducting long-term studies or quick experiments, using a stable microscope minimizes the risk of measurement errors due to misalignment or mechanical issues.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体